Despite the importance of both kinds of social capital and collaborative networks and some notable insights provided by existing research from many different perspectives, existing understanding on the phenomenon was still fragmented and incomplete.
In order to contribute to developing a more comprehensive understanding, this research project examined the impact of both kinds of collaborative networks- internal and external social capital- on innovative ambidextrous strategies and the innovative performance of firms.
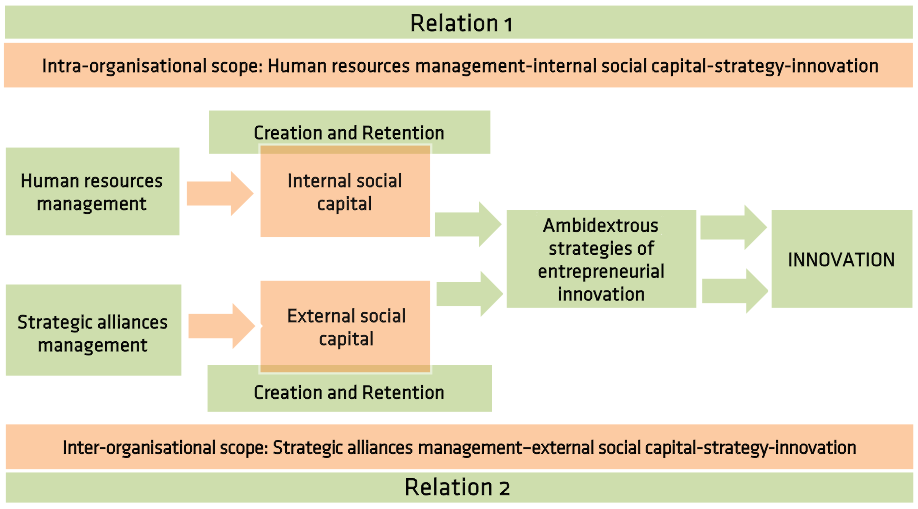
To that end, two relations were analyzed (see figure):
- In Relation 1, we examined the influence of human resource management in the consolidation of internal social capital, in particular, social capital generated among the core employees of the organization and its impact on the innovation capacity of the organization.
- In Relation 2, we studied how strategic R&D alliances can favor the maintenance of external social capital. In particular, we focussed on those collaborative networks established between firms and research and technological centers in order to achieve superior organisational performance in the form of innovation.
In this research project, two different methodologies were used:
- Relation 1 was studied using a quantitative methodology, based on information gathered through a survey on a large sample of innovative Spanish firms (which received financial support from the CDTI in the last years).
- Relation 2 was studied using a qualitative methodology, in particular, the case study methodology focusing on “Dibaq Group as the lead firm of the Acuisost Project- Towards a Sustainable Aquaculture”.
The Acuisost Project was a R&D consortium created under the Spanish CENIT Programme, in which multiple firms and research and technological centers take part. In particular, we started with 16 technological centers (universities and others) that collaborate in the consortium and we studied in-depth the collaborative relationship of DIBAQ and CARTIF.